- Home
- INFUSION SECTION
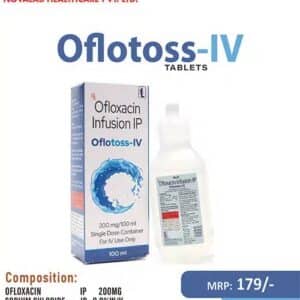
- Ofloxacin Injection


Ofloxacin Injection is a broad-spectrum antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. It belongs to the fluoroquinolone class, inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, crucial for DNA replication and repair. By disrupting these processes, Ofloxacin halts bacterial growth and induces cell death. Administered intravenously, it’s effective against respiratory, urinary tract, skin, and soft tissue infections. Careful dosage adjustment is required for renal impairment. While generally well-tolerated, side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, and headache can occur. Caution is advised in patients with a history of tendon disorders. Consultation with a healthcare professional is crucial for proper use and monitoring.
Benefits of Using Ofloxacin Injection
Ofloxacin Injection provides notable benefits in treating bacterial infections. As a potent fluoroquinolone antibiotic, it exhibits broad-spectrum activity against various bacteria. Rapid absorption and distribution contribute to its efficacy in treating respiratory, urinary tract, and skin infections. Its mechanism of action, inhibiting DNA gyrase, disrupts bacterial DNA replication, ensuring bactericidal effects. The injectable form ensures quick and reliable delivery. Ofloxacin is particularly valuable for its versatility, addressing both Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms. While generally well-tolerated, consultation with a healthcare professional is crucial to determine proper dosage and assess potential interactions, ensuring optimal therapeutic outcomes.
How to Use Ofloxacin Injection
Ofloxacin Injection is typically administered by a healthcare professional in a clinical setting. The dosage and duration depend on the type and severity of the infection. Before use, the vial is reconstituted with a compatible diluent. The injection is then given intravenously, allowing for rapid absorption. Strict adherence to the prescribed dosage and schedule is crucial for optimal effectiveness. Patients must complete the entire course, even if symptoms improve, to ensure complete eradication of the infection. Regular monitoring for any adverse reactions is advised, and any concerns or side effects should be promptly discussed with a healthcare professional.
How Ofloxacin Injection Works
Ofloxacin Injection operates by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, crucial enzymes for DNA replication and repair. As a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, Ofloxacin disrupts these processes, preventing the unwinding of bacterial DNA and impeding its replication. This leads to the inhibition of bacterial growth and induces cell death. Its broad-spectrum activity encompasses Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, making it effective against various infections. Administered intravenously, Ofloxacin ensures rapid and reliable delivery to target sites. However, careful use is advised to prevent antibiotic resistance, and healthcare professionals determine its appropriateness based on the specific bacterial strain and clinical context.
Precautions While Using Ofloxacin Injection
While using Ofloxacin Injection, precautions are crucial. It should be administered under healthcare professional supervision in a clinical setting. Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to fluoroquinolones require careful consideration. Tendon inflammation and rupture have been reported, particularly in the elderly, necessitating caution during treatment. Use in patients with myasthenia gravis is generally avoided. Ofloxacin might cause central nervous system effects, and caution is advised in patients with a history of seizures. Adequate hydration is recommended to prevent crystalluria. Monitoring for potential side effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances or allergic reactions, is essential. Consultation with a healthcare professional is vital for proper use and monitoring.
Side Effects of Using Ofloxacin Injection
Ofloxacin Injection might induce side effects, including gastrointestinal issues like nausea and diarrhea. Central nervous system effects such as headache and dizziness are possible. Tendon inflammation and rupture, although rare, require immediate medical attention. Photosensitivity reactions might occur, warranting sun protection measures. Rare but serious side effects involve allergic reactions, seizures, or liver dysfunction. Long-term use can contribute to bacterial resistance. Caution is advised in patients with myasthenia gravis. Monitoring for adverse effects, especially in vulnerable populations, and prompt consultation with a healthcare professional in case of unusual symptoms are crucial. This is not an exhaustive list, and individual responses might vary, necessitating professional guidance.
Related products
We are a research-based pharmaceutical company. The mission of Novalab Healthcare is to improve the health of the Indian community by providing them with quality
Quick Links
Location
- Plot No-208, Industrial Area Phase 1, Panchkula, Haryana 134113
- Novalab7777@gmail.com
- +91-9570599567
- +91-9115604598