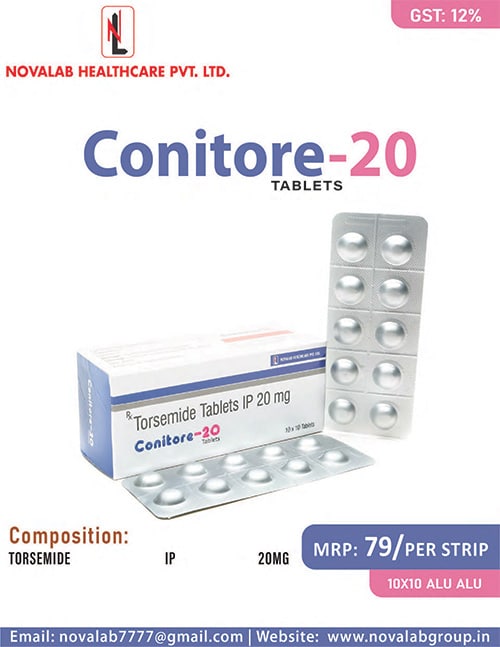
CONITORE-20
Categories: CARDIAC/DIABETIC PRODUCTS, TABLETS / CAPSULES / SOFT GEL
Enquiry about CONITORE-20
Related products
We are a research-based pharmaceutical company. The mission of Novalab Healthcare is to improve the health of the Indian community by providing them with quality
Quick Links
Location
- Plot No-208, Industrial Area Phase 1, Panchkula, Haryana 134113
- Novalab7777@gmail.com
- +91-9570599567
- +91-9115604598
Map
Copyright by © 2025 Novalab Healthcare | Web Development and Marketing By Web Hopers
Contact Us